EAM Tool APIs Using EAS Cloud as an Example
Everything You Need to Know About the Basics of EA Tool APIs.
Enterprise Architecture Tools - APIs
Enterprise Architecture Management (EAM) tools can significantly optimize and automate processes. A key component of this is the use of APIs. In this article, we demonstrate how to retrieve basic data using APIs with the EAS Essential Cloud Enterprise Architecture software.
With APIs, EAM software can be programmatically accessed. We focus on the following aspects:
1 Configuration of Essential Cloud 2 Necessary API Parameters for Access 3 Authentication 4 Retrieving Applications
The Essential Project is listed in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for EAM tools under the company name Enterprise Architecture Solutions as a visionary. The software is available as a commercial SaaS solution and as a free open-source version.
Configuring EAS
To access EAS via the API, you need to create a technical user within the application. Users synchronized from a directory are not suitable as API users.
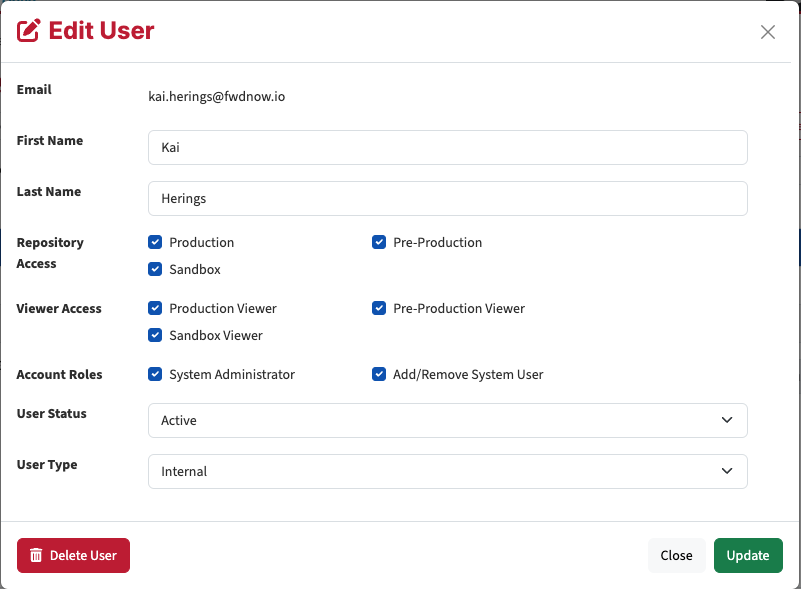
The technical user must:
- Have “System Administrator” privileges
- Be set as “internal”
Essential API Parameters for Access
To access the API, you need the following information:
- Username of the technical user
- Password
- EAS API Key
- EAS Repository ID
The API Key is found in the administrator settings:
Located under “TENANT API KEY”:

EAS Cloud typically contains multiple repositories where EAM data is stored. To access the correct repository, the appropriate Repository Key must be identified:
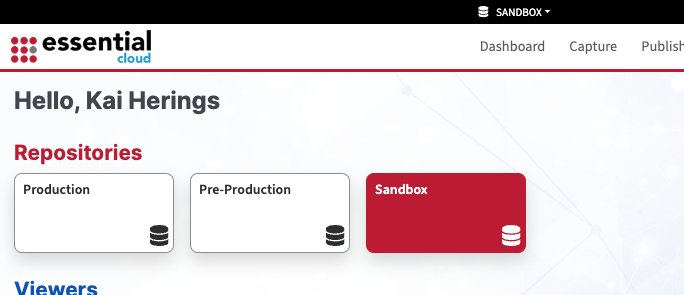
Select the desired repository from the overview and click “Capture”:

The Repository ID can be copied from the URL: “4141414141414141414141”.
Authentication in EAS
EAS authentication follows the OAuth 2.0 security schema:
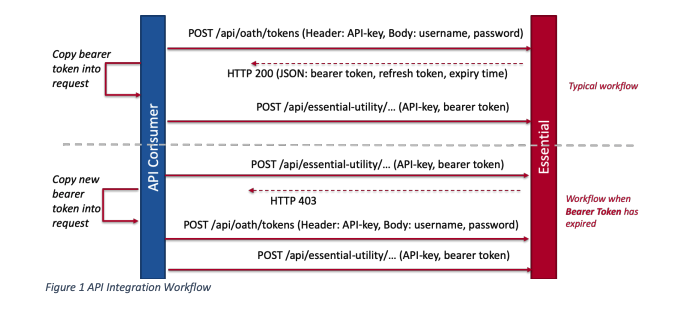
Below is an example authentication script for the EAS instance:
import requests
import json
BASE_URL = "https://forwardnow.essentialintelligence.com/api"
TOKEN_URL = f"{BASE_URL}/oauth/token"
API_KEY = "DEADBEEFDEADBEEF..."
USERNAME = "kai.herings@fwdnow.io"
PASSWORD = "secret"
def get_bearer_token():
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json", "x-api-key": API_KEY}
payload = {"grantType": "password", "username": USERNAME, "password": PASSWORD}
response = requests.post(TOKEN_URL, headers=headers, json=payload)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()["bearerToken"]
else:
print(f"Error retrieving token: {response.json()}")
return None
This script generates the Bearer Token, required for subsequent API access.
Retrieving Applications
Applications are located in the metamodel under the object “Application Provider Role”:
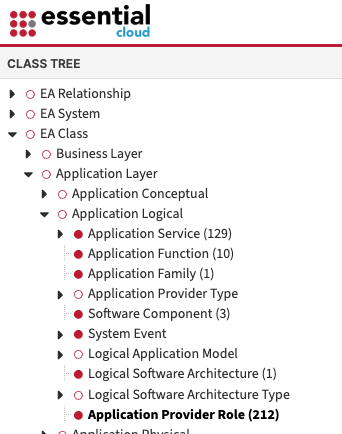
Below is an example script for fetching application names:
def fetch_applications():
bearer_token = get_bearer_token()
if not bearer_token:
print("Failed to retrieve a valid bearer token.")
return
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json", "x-api-key": API_KEY, "Authorization": f"Bearer {bearer_token}"}
response = requests.get(APPLICATIONS_URL, headers=headers)
data = response.json()
names = [instance.get("name") for instance in data.get("instances", [])]
for i, name in enumerate(names, start=1):
print(i, name)
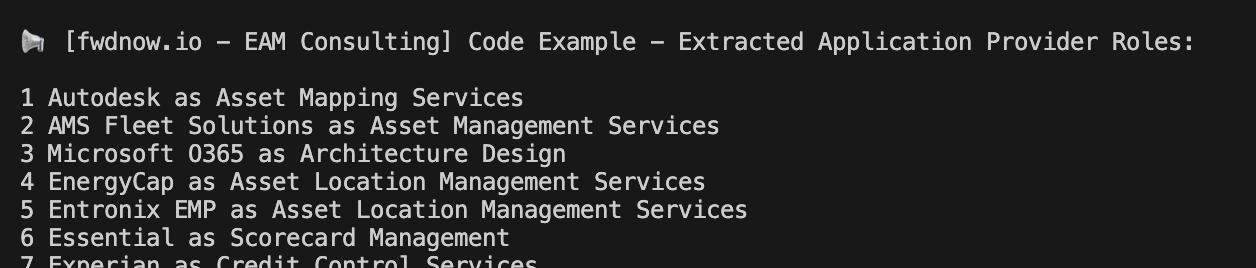
print("\n📢 [fwdnow.io - EAM Consulting] Extracted Application Provider Roles:\n")
fetch_applications()
The script outputs the application names to the console:
Use Cases for API-Integrated EAM Solutions
API integration into EAM systems offers numerous benefits:
1. Software Procurement & License Management
Automatically record new software purchases and align them with the existing IT architecture.
2. Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Management
Track test environments and PoCs directly within the EAM solution.
3. Automated Repository Documentation
Automatically document new GitLab or GitHub repositories within the EAM solution.
4. IT Service Management (ITSM) Integration
Integrate with ITSM tools (e.g., ServiceNow) for continuous architecture documentation updates.
5. Synchronization with Cloud Environments
Sync cloud resources (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) with the EAM solution for transparency.
By leveraging API integration, EAM solutions can serve as a central architecture management platform, significantly reducing manual maintenance efforts. This saves time, improves data quality, and enhances collaboration between IT and business teams.
Want to learn more?
Book a 1:1 Session
Kai Herings
Senior consultant
Optimize alignment between IT and business with expert advice and clear strategies.
